Practice and summary.
001 TwoSum
002 AddTwoNumbers
003 Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
001 TwoSum
Description
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target. You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
Example:
Better Approach (Hash Table)
Idea
Hash Table O(n) in time and space Best way to maintain a mapping of each element in the array to its index
Iterate and insert elements into hash table. At the same time, check if current element’s complement already exists in the table.
Code
std::unordered_map: (hashtable) insert and access in O(1) (if a collision occurred, a look up could degenerate to O(n) time)std::map: elements are sorted by the key, insert and access is in O(log n). Usually the STL internally uses red black trees for ordered maps
Trick A vector ordered from low to high is required to return(?), I didn’t sort my vector by using vector<int> {hash_table[complement], i}; but it just works. (Accepted)
My Approach (Sort and Match)
Idea
- Sort O(nlogn) I used
structto store thenumber&indexand write acmpfunction forsort. - Iterate O(n) Assume
target = sort_nums[i] + sort_nums[j] (i < j), iterate the sorted array from two direction: begin->end(i) and end->begin(j) until find the answer.
Code
|
|
002 AddTwoNumbers
Description
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list. You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Approach (Simulate digits-by-digits sum)
Idea
Simulate digits-by-digits sum starting from the head of list O(max(m, n)) in time and space, m and n represents the length of l1 and l2 respectively
Code
- Cleaner but slower. (49ms, 56.21%)
- Only one loop but
4 * max(m, n)times judgement for null pointer
|
|
- Faster but longer(redundant). (38ms, 87.27%)
- Readable:
curCarryandlastCarry - Three loops but
2 * max(m, n) + m + ntimes judgement for null pointer. Save time whenm >> norn >> m.
|
|
Note
- Bad ides: Find out the two numbers, add them directly which may results in overflow when the sum is large.
- Use
p->next = ...;: p is a pointer used for iterating, oncep = head;, we cannot assign it again likep = new ListNode(val);which will make p a new pointer.
003 Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
To know is easier than to do! Code again!
Description
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Examples: Given "pwwkew", the answer is "wke", with the length of 3. Note that the answer must be a substring, "pwke" is a subsequence and not a substring.
Approach (Sliding Window Optimized)
Idea
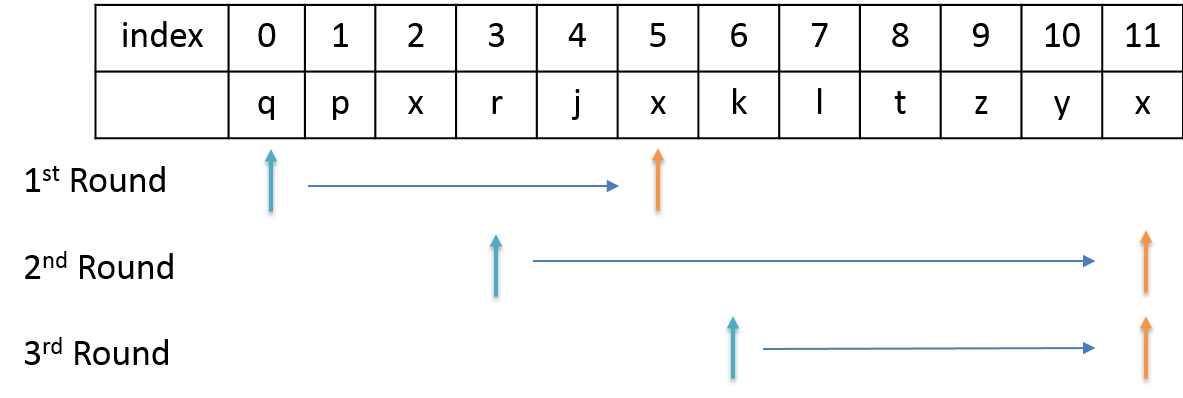
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity : O(n). Index j will iterate n times.
Space complexity (Table): O(m). m is the size of the charset.
Code
vector<int> charToIndex(256, -1);Because the charset is rather small(total number of Character in Extended ASCII table is 256 (0 to 255)), we can replace the Map(std::unordered_map) with an integer array as direct access table. (Speed: 38ms -> 26ms)int i = -1;reduces the calculate of+which saves time. For example,j - i + 1. (Speed: 26ms -> 18ms/93.52%)
|
|